Our projects
Contributing to the preservation and sustainable management of Tapia’s natural forests
Project TAPIA – Madagascar
On deployment
Madagascar’s Itasy region covers an area of 7,000 km², of which less than 3% is currently forested.
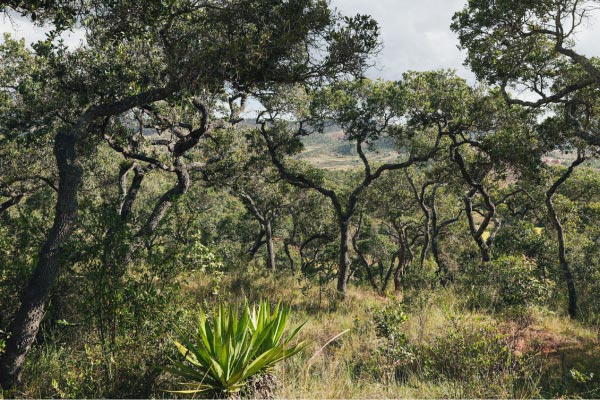
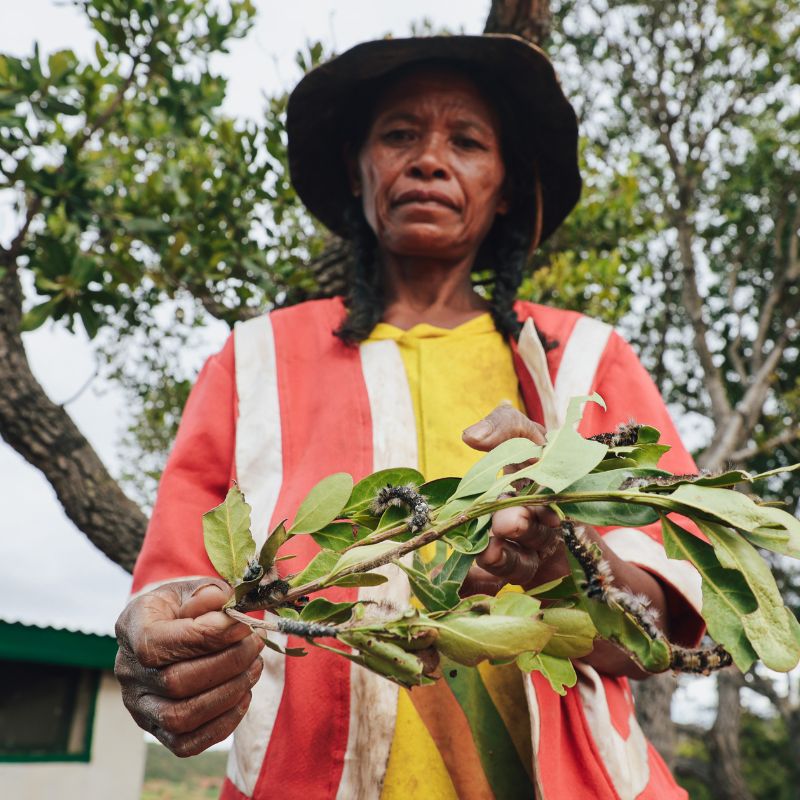
The Tapia forest, which is one of the Great Island’s endemic and remarkable ecosystems, plays a key ecological role here, preserving water sources, stabilising watersheds, protecting soils against erosion and maintaining their fertility, and regulating the local microclimate. It is also home to an abundance of biodiversity and provides resources on which local communities are heavily dependent. In particular, the Tapia is the main habitat of an endemic species of wild silkworm – the landibe – which feeds mainly on its leaves. The landibe forms cocoons of wild silk, which are traditionally used to make handicraft textiles (clothes, scarves, shrouds, festive garments, etc.).

Context
In the Itasy region, the forests of Tapia (an endemic tree) provide resources on which the local grassroots communities (also known as VOI – Vondron’Olona Ifotony), to whom the Malagasy state has delegated management, depend heavily. In particular, this ecosystem is home to an endemic species of wild silkworm, whose silk cocoons are traditionally used to make handicraft textiles.
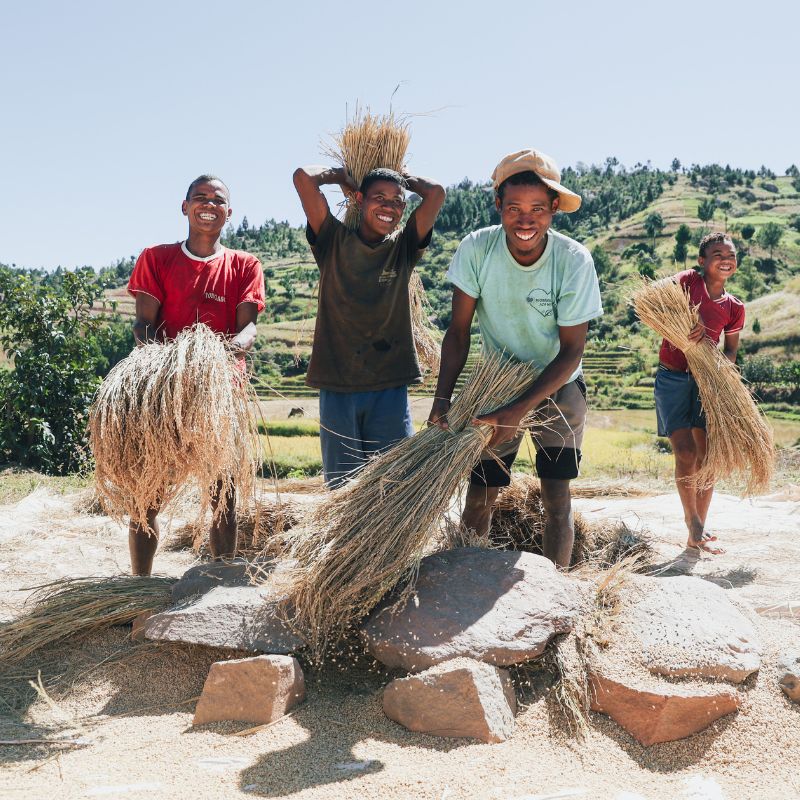
Today, the massive destruction of the Tapia forests and their over-exploitation (for fuelwood and agriculture) are threatening the biodiversity of these ecosystems. The VOIs, which manage these resources, lack the resources (technical, material and financial) to ensure local monitoring and the application of sustainable management rules. In addition, demographic pressure and rural poverty are leading local communities to fall back on the remaining forests to improve their daily livelihoods.
Key figures
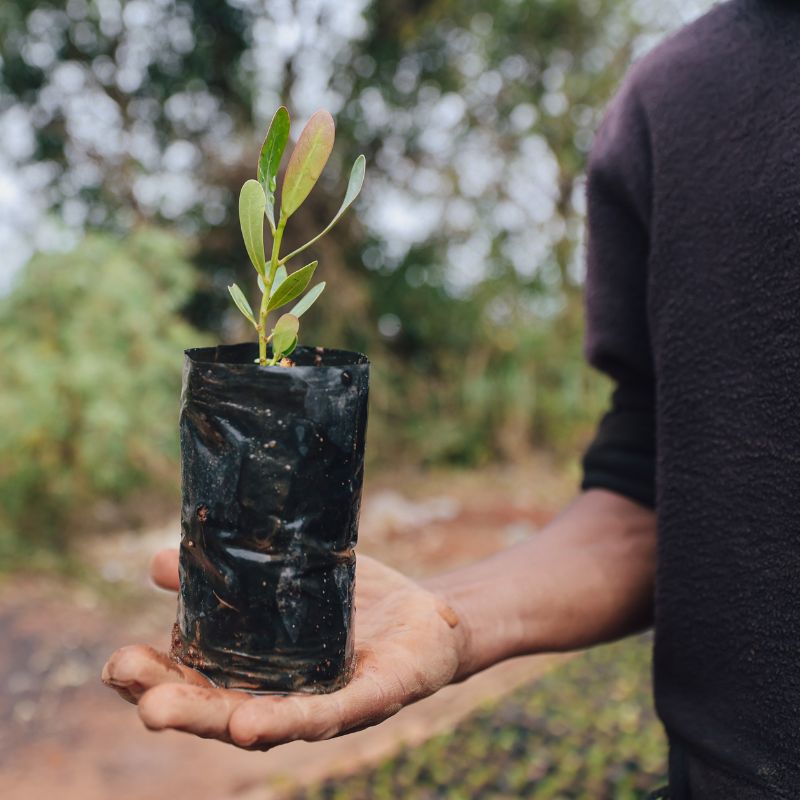
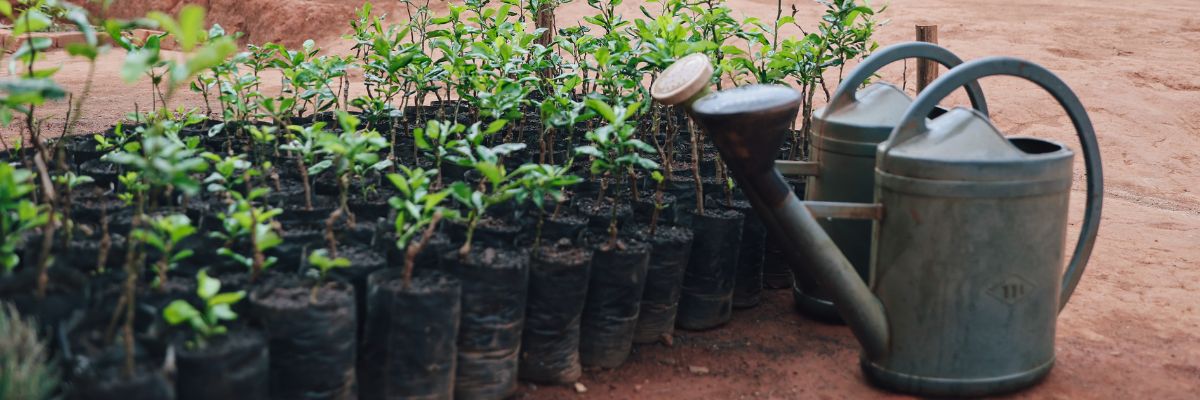
Since 2022, the programme has been :

3.7 millions
of trees planted

1310
hectares reforested
Photos © Christophe Michel
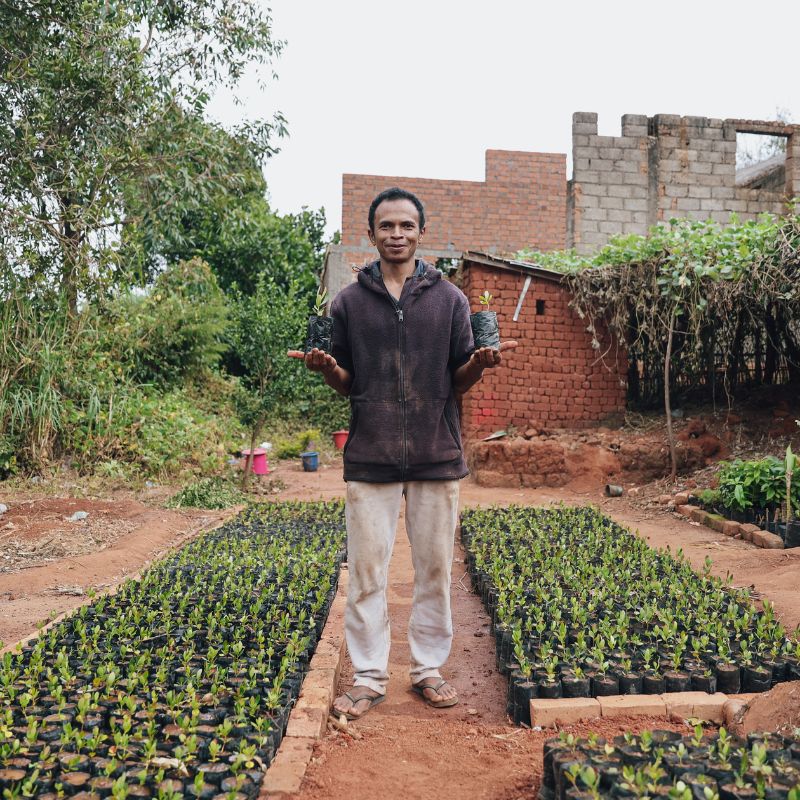
« The TAPIA project is important to me because it has a positive impact on the forest around me and on the income of my community. »
Jean Émile, Chairman of a VOI
Financed by


Implementation partner








