Our projects
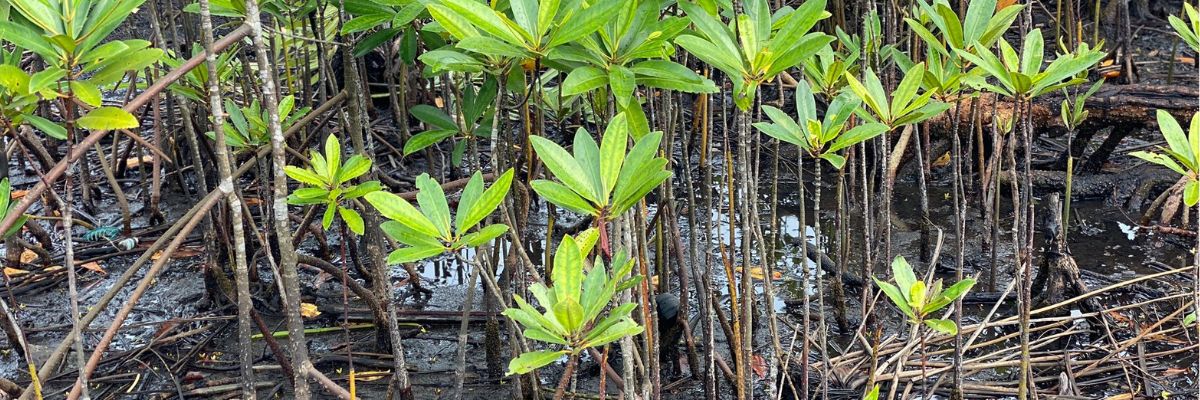
Restoring mangrove ecosystems
Project CAMERR – Cameroon
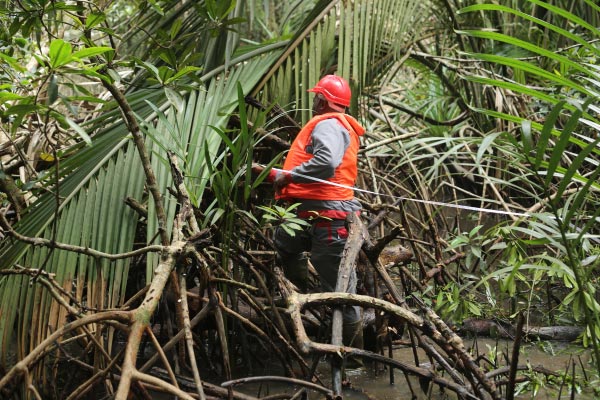
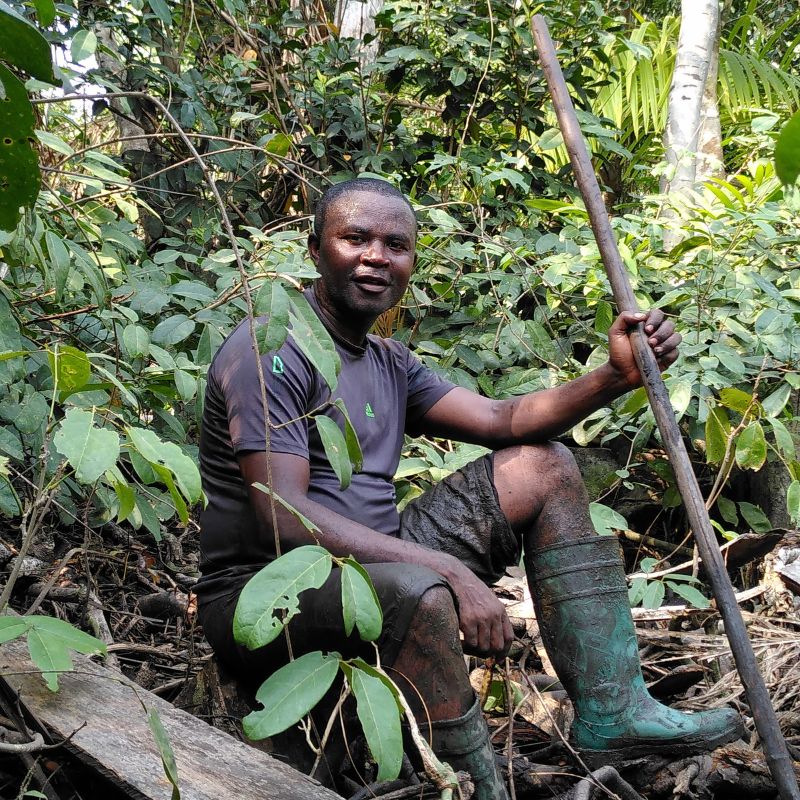
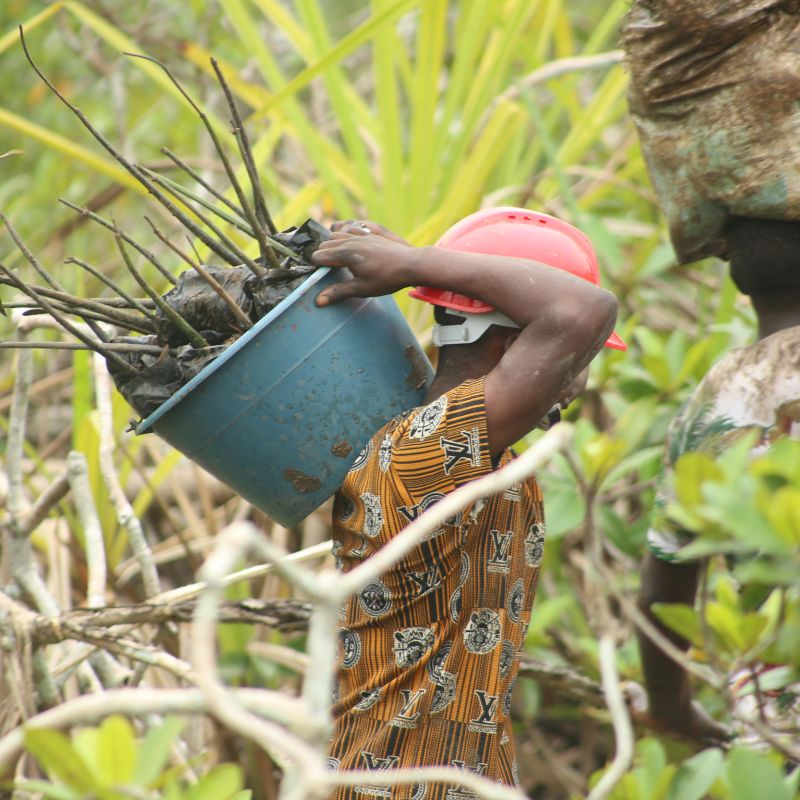
On deployment
The project area is home to several types of vegetation and habitats that are important for maintaining biological diversity in relation to its mangroves. The Cameroon estuary, in which the metropolis of Douala is located, is estimated to contain around 203,600 hectares of mangroves, associated coastal forests, plantations and dwellings and associated non-vegetated land, including 93,550 ha of land ‘purely’ covered by mangroves.
Cameroon’s coastal zone is also home to a varied fauna including birds, elephants, antelopes, chimpanzees, monkeys and crocodiles, as well as manatees, aquatic mammals, notable species of turtles, reptiles and molluscs and shrimps.

Context
The Wouri estuary (Douala region) is now seeing its mangrove ecosystems severely degraded: 70,000 ha of mangrove forests are thought to have been decimated in Cameroon between 1980 and
2006. This is due to demographic pressure, urbanisation, fish processing, sand extraction, insufficiently coordinated policies and coastal economic development programmes.
This degradation is worsening at the expense of the biodiversity that inhabits this ecosystem, and the activities of the local populations: less fishing, flooding, rising temperatures, etc.
Key figures
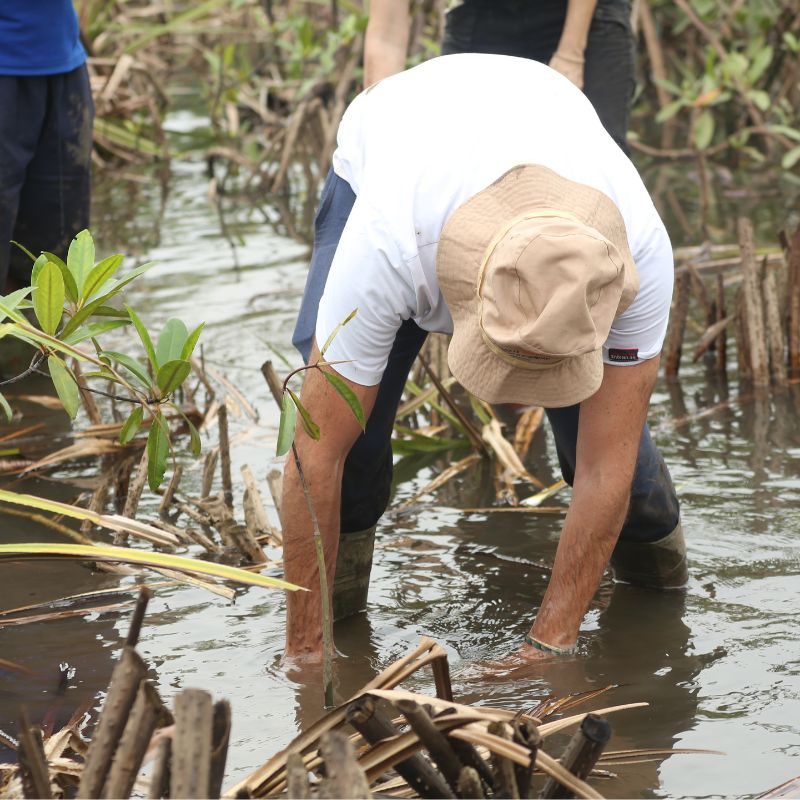
Since 2020, the programme has included :

707000
trees planted

232
reforested hectares
« The restoration of mangroves through CAMERR has been warmly welcomed by local communities. They saw the project as a guarantee of security of tenure through the creation of community forests. »
Diyouke Mibog Eugène, CAMERR Project Manager at CWCS (Cameroon Wildlife Conservation Society)
Implementation partner